In August 2020 Emma Hagström Molin organized a two-day ZOOM workshop about provenance with the support of the Centre for Integrated Research on Culture and Society (CIRCUS) of Uppsala University (Sweden). Her current research on the material conditions for historical research during the nineteenth century is funded by an international postdoctoral fellowship of the Swedish Research Council, and she had convened a diverse and lively group of presenters and listeners. As the ZOOM workshop was not open to the public, it does not have a website with detailed information about its program and presenters.
On the second day the workshop effectively closed with a question posed by Claes-Fredik Helgesson, the director of CIRCUS. Helgesson ruminated whether mapping could help with organizing the bits and pieces of our collective knowledge of the various aspects of provenance, thereby analyzing and elucidating how the concept’s meaning and its epistemological status in classification schemes has evolved in diachronic and synchronic perspectives, over time and across space. Helgesson’s use of the word “mapping” was intriguing. It made me wonder about the viability of a future Digital Humanities (DH) project which would employ visualization tools for constructing a history of the concept of provenance, while tracking changing practices of provenance research in a range of disciplines in the Humanities and the Sciences.
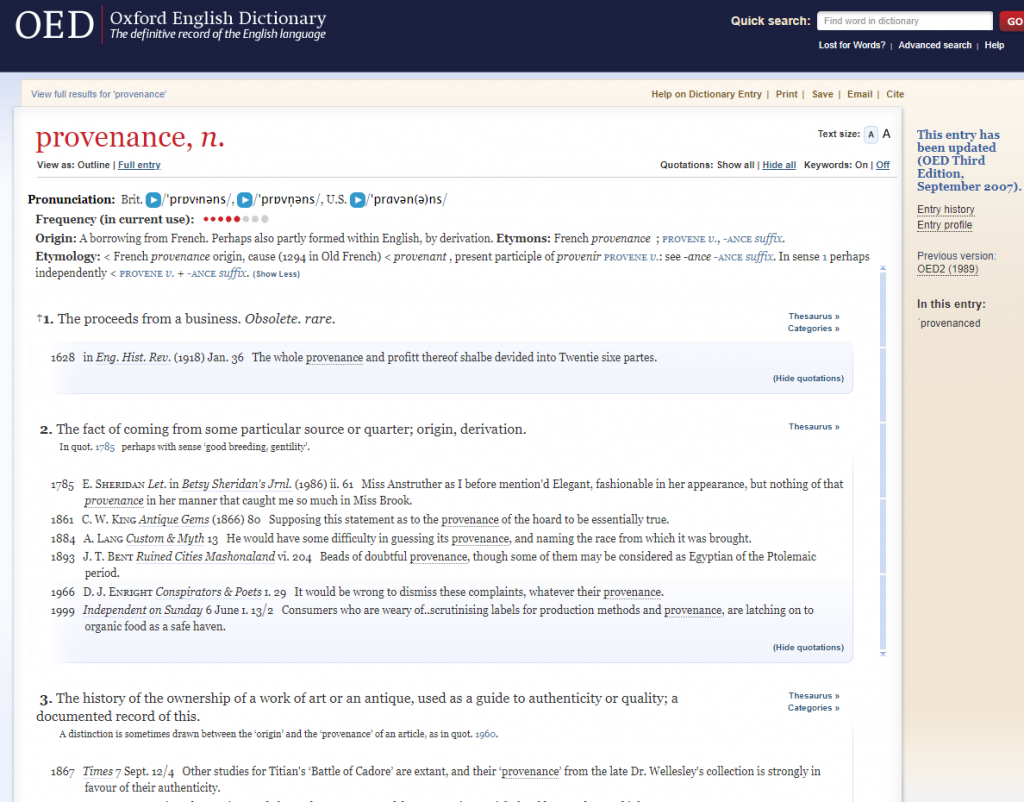
Hagström Molin had opened her introduction to the workshop with a reflection on the history and etymology of the word “provenance,” bringing into the discussion how Gail Feigenbaum and Inge Reist define the word in their introduction to Provenance: An Alternative History of Art (Los Angeles: Getty Research Institute, 2012, 1 and 4 n.1). Feigenbaum and Reist state that in the Oxford English Dictionary (OED) the first documented use of provenance occurred in 1785, when the word served as shorthand for “history of ownership,” with the extended meaning of “documented record.” Unfortunately, Feigenbaum and Reist do not identify date and format (that is, printed or digital) of the consulted OED version. More important, though, is their astute observation that “[o]n the face of it, we all know what provenance means” (p. 1). A short survey of recent English-language scholarship confirms that the word’s meaning is indeed perceived as being self-evident – which usually is a red flag that things are more complicated than we would like them to be. Nick Pearce and Jane C. Milosch open their introduction to Provenance and Collecting (London: Rowan & Littlefield, 2019) with this breezy statement: “The most basic definition of the word provenance is ‘place of origin’ from the French provenir, ‘to come from,’ and before this, the Latin provenire: pro, ‘forth’ and venire ‘come.’ Increasingly, the word has come to be closely associated with the history of creation and ownership of a specimen, artifact, or work of art” (p. xv). Unlike Feigenbaum and Reist, Pearce and Milosch do not provide a reference for these etymological and historical details, and yet they draw attention to the word and its meaning. Victoria Reid does not comment on the word itself in her entry on “Provenance” in Grove Art Online (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2003, updated 2016, https://doi.org/10.1093/gao/9781884446054.article.T069868), and neither does David Pearson in his handbook about Provenance Research in Book History (2d ed., Oxford: Bodleian Library, 2019).
My own reading of the entry on provenance in the current version of the OED Online, which provides the text of the third revised edition of 2007, differs from that offered by Feigenbaum and Reist, but they may have consulted an earlier edition of the OED.
NB – The entry’s remainder is not shown as it merely provides more citations for the word’s third meaning.
The note on provenance’s origin includes a warning: “A borrowing from French. Perhaps also partly formed within English, by derivation.” The first identified meaning draws on a 1918 article for the citation of a 1628 source to conclude that in the early modern era the word provenance was used in business transactions to indicate “the source of profit.” This first meaning, though, is marked as rare and nowadays obsolete. As regards the documented use in 1785, highlighted by Feigenbaum and Reist, the citation is presented as evidence for the second meaning: “[t]he fact of coming from some particular source or quarter; origin, derivation.” But the OED editors add the disclaimer that the 1785 citation may represent a slightly different usage than that illustrated by the following citations for the nineteenth and twentieth century. The oldest given citation for the third meaning, which represents the word’s contemporary usage by art historians as contextualized by Feigenbaum and Reist, was published in 1860.
I draw three conclusions from this linguistic evidence. The first is that it offers a timely reminder about the importance of French as one the languages of medieval and early modern England. A word that looks like a borrowing from French does not automatically point to Franco-British contacts in the late eighteenth century. The second conclusion is that it directs attention to the close relation between provenance’s meaning in the seventeenth and eighteenth century. While the seventeenth-century meaning was narrow and precise, the eighteenth-century meaning had broadened and became more general. The third conclusion is that it presents the evolution of provenance’s meaning as metonymy, if its history is read backwards, from the present to the past: an object acquires value when authenticity is confirmed and owners are known, thereby becoming a source of profit.
Against this backdrop I offer the working hypothesis that the concept of provenance – defined as the chain of ownership, whether legal or illegal, through which a mobile or immobile object was transferred between people – is present in every society whose members can own private property and whose economy supports markets and a practice of individual collecting. While more comparative research would be necessary to identify the role of conspicuous consumption for practices of individual collecting, I hasten to add that I am not arguing that owning individual property is an anthropological constant. In order to facilitate a comparative approach based on a range of disciplines from the Humanities and the Sciences, I would suggest to employ a heuristics that draws on semiotics to distinguish between word (signifier), meaning (signified), and concept (referent). This heuristic strategy would allow for investigating changes and differences between languages, eras, and locations, thereby revealing developments over longer stretches of time. The concept of provenance is posited to be stable, but words and meanings change, be it in conjunction or be it separately. On the one hand, a word remains in use, but its meaning is new; an example would be looting. On the other hand, the meaning is retained, although it is now attached to a different word; e.g., we approve of national heritage but shun the common good. One of the possible outcomes of this heuristic approach could be a representation of the different aspects of the concept of provenance, for example, through three different maps visualizing words, meanings, and the changing relations between them.
Last updated, 29 August 2020