Hijab Mandate and Women’s Agency: Navigating Autonomy in Afghanistan
Article by Staff Writer Nazeela Elmi
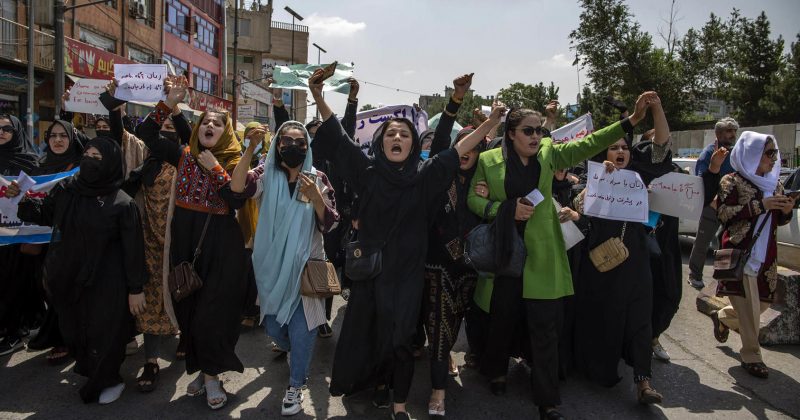
Image by Kiana Hayeri from The New York Times
In September 2021, a few days after the Taliban takeover of Afghanistan, a group of women in black head to toe niqab covering went out in Kabul University and Kabul streets to demonstrate their support for the Taliban regime. Many rightfully assumed that, as all of the signs held by the protestors had the same blueprint and all of them wore the same article of clothing, the demonstrations were staged by the Taliban against women who held anti-Taliban views and who protested following the collapse of the former Afghan government. This kind of covering was unprecedented in Kabul or anywhere in Afghanistan.
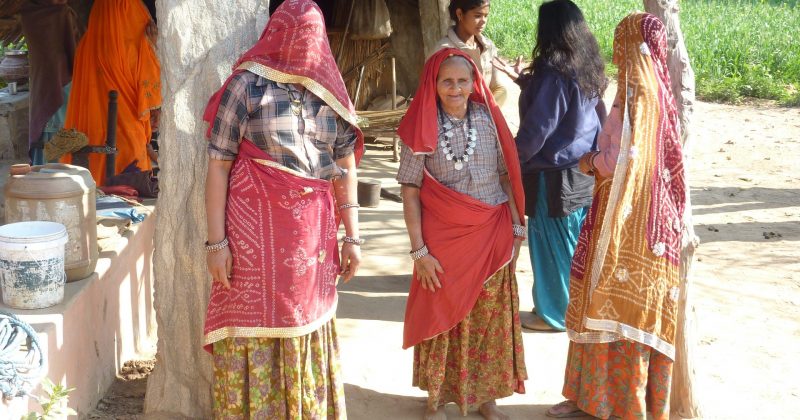
Women’s veiling varies across Afghanistan given their roles in society, agriculture, throughout their historical junctures, and in various geographical and cultural regions. Veiling has not been mandated under the law in the former government in Afghanistan, though the burqa was imposed during the first rule of...