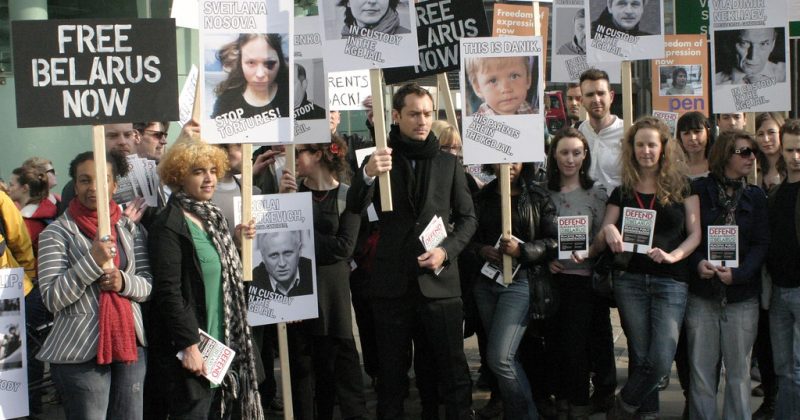
Anti-Media Law in Belarus: A Dreadful Attack on Press Freedom
By guest contributor Astha Bhattacharya*
INTRODUCTION
Belarus ratified its new anti-media law in May 2021, primarily aimed at limiting journalists' freedom of expression and quelling protests against the Belarusian government. The new law makes it illegal for the media to report on any unauthorised public gatherings or to publish opinion polls unless the results have been approved by the government. This law also grants the government the authority to shut down media companies without judicial orders, which were previously necessary. Human rights organisations have slammed this law and the subsequent shutdowns of independent media outlets, claiming that the bill is intended to silence the growing criticism against the Belarusian government.
The new law was introduced in the aftermath of the 2020 uprisings against President Alexander Lukashenko, who has been in power since Belarus broke away from the Soviet Union in 1994. There has not been a single free and fair election in Belarus since 1995, according to the Organisation for Security and Co-operation in Europe. Additionally, Lukashenko...